Hydrocele Treatment
Hydrocele Treatment
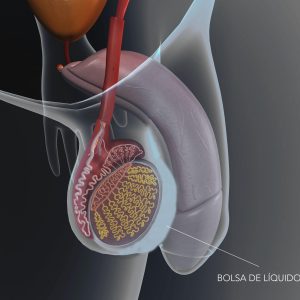
Hydrocele refers to swelling of the scrotum in men due to fluid filling it. Even though it is not a serious health issue, it can cause embarrassment and discomfort. It is more common for male infants to have hydroceles than for adult males, and there are treatments available to solve the problem.
Hydrocele : how common is it ?
A hydrocele affects about 10% of newborn male infants and usually goes away without treatment within a year. Adult men rarely develop hydroceles, and they often disappear on their own.
Who is at risk of developing a hydrocele ?
Adolescent and adult men can also suffer from the condition, although it is much more common in baby boys.
How does a hydrocele develop ?
Although hydroceles can occur at any age, they are more common in newborns. An underlying injury or even inflammation can also cause them to develop, even when there are no underlying causes. In most cases, hydroceles are just an inconvenience – but they do not last long.
Among infants
As a child\’s pregnancy progresses, the testicles descend from the abdomen into the scrotum. Upon descent, the testicles are held in the scrotum, which is a sac of skin.
There is a naturally occurring sac that contains fluid around each testicle during development. After the baby\’s first year, the sac naturally closes and the fluid inside is absorbed by the body. Babies with hydrocele, however, do not experience this. Prematurely born babies are at a higher risk of developing hydrocele.
Among adults
It is also possible for men over 40 years of age to develop hydroceles later on in life. Hernias can cause them, but they are less common. Generally, it is either inflammation or an inability to reabsorb fluid from the tunica vaginalis. Dysfunction with the epithelial cells in the sac can lead to excess fluid production and reabsorption.
It is also possible to develop hydroceles due to inflammation or injury in the scrotum or along the channel. A condition such as epididymitis or an infection can cause inflammation.
Which types of hydrocele are there ?
The types of Hydrocele are as follows :
- Communicating hydrocele : A type of hydrocele in which fluids in the abdominal cavity are in contact (communicating). A communicating hydrocele results from a failure of the processus vaginalis (the thin membrane that extends through the inguinal canal and into the scrotum). Both a hernia and a hydrocele can develop if this membrane remains open. There will be swelling or enlargement of the child\’s scrotum, which may change in size throughout the day.
- Non-communicating hydrocele :The non-communicating hydrocele is one in which the inguinal canal has closed but there is still extra fluid around the testicle in the scrotum. A condition like this may be present at birth or develop years later for no apparent reason. The size of a noncommunicating hydrocele usually remains the same or grows very slowly.
- Nuck’s hydroceles : are a rare type of swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin, which can occur in people without testicles. They can occur in the lining of the pelvic wall. It is difficult to diagnose and treat this condition because it can be mistaken for ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and a host of other conditions.
What is the process of diagnosing a hydrocele?
Dr. Khilchand Bhangale at Alpha One Hospital can diagnose a hydrocele in a child or adult through a combination of tests and observations, including :
- Physical exam : This may include watching how the bulge in the groin area changes when the patient coughs or shining a light through the scrotum to check for any fluid collection..
- The use of an imaging test, such as an ultrasound.
What complications can a Hydrocele cause ?
In most cases, hydrocele is not dangerous and does not affect fertility. Nonetheless, a hydrocele might be associated with an underlying testicular condition that can lead to complications, such as :
- Infection or tumor : The production or function of sperm may be reduced by either of these factors.
- Inguinal hernia : Life-threatening complications can occur when the loop of the intestine becomes trapped in the abdominal wall
हायड्रोसेल उपचार
हायड्रोसेल म्हणजे पुरुषांमध्ये स्क्रोटममध्ये द्रव भरल्यामुळे सूज येणे. जरी ही एक गंभीर आरोग्य समस्या नसली तरी, यामुळे लाज आणि अस्वस्थता निर्माण होऊ शकते. प्रौढ पुरुषांपेक्षा पुरुष अर्भकांमध्ये हायड्रोसेल्स असणे अधिक सामान्य आहे आणि समस्येचे निराकरण करण्यासाठी उपचार उपलब्ध आहेत.
हायड्रोसील : ते किती सामान्य आहे ?
हायड्रोसेल 10% नवजात पुरुष अर्भकांना प्रभावित करते आणि सामान्यतः एका वर्षाच्या आत उपचाराशिवाय निघून जाते. प्रौढ पुरुष क्वचितच हायड्रोसेल्स विकसित करतात आणि ते स्वतःच अदृश्य होतात.
हायड्रोसेल विकसित होण्याचा धोका कोणाला आहे?
पौगंडावस्थेतील आणि प्रौढ पुरुषांना देखील या स्थितीचा त्रास होऊ शकतो, जरी हे लहान मुलांमध्ये अधिक सामान्य आहे.
हायड्रोसेल कसा विकसित होतो?
जरी hydroceles कोणत्याही वयात उद्भवू शकतात, ते नवजात मुलांमध्ये अधिक सामान्य असतात. अंतर्निहित दुखापत किंवा जळजळ देखील त्यांना विकसित करण्यास कारणीभूत ठरू शकते, जरी कोणतीही मूलभूत कारणे नसतानाही. बहुतेक प्रकरणांमध्ये, हायड्रोसेल्स फक्त एक गैरसोय आहे – परंतु ते फार काळ टिकत नाहीत.
लहान मुलांमध्ये
लहान मुलाची गर्भधारणा जसजशी वाढत जाते तसतसे अंडकोष पोटातून अंडकोषात उतरतात. खाली उतरल्यावर, अंडकोष अंडकोषात धरले जातात, जी त्वचेची थैली आहे.
एक नैसर्गिकरित्या उद्भवणारी थैली आहे ज्यामध्ये विकासादरम्यान प्रत्येक अंडकोषभोवती द्रव असतो. बाळाच्या पहिल्या वर्षानंतर, पिशवी नैसर्गिकरित्या बंद होते आणि आतला द्रव शरीराद्वारे शोषला जातो. हायड्रोसेल असलेल्या बाळांना मात्र याचा अनुभव येत नाही. अकाली जन्मलेल्या बाळांना हायड्रोसेल होण्याचा धोका जास्त असतो.
प्रौढांमध्ये
40 वर्षांपेक्षा जास्त वयाच्या पुरुषांना नंतरच्या आयुष्यात हायड्रोसेल्स विकसित होणे देखील शक्य आहे. हर्निया ते होऊ शकतात, परंतु ते कमी सामान्य आहेत. सामान्यतः, ही एकतर जळजळ असते किंवा ट्यूनिका योनिलिसमधून द्रव पुन्हा शोषण्यास असमर्थता असते. थैलीतील एपिथेलियल पेशींसह बिघडलेले कार्य जास्त द्रव उत्पादन आणि पुनर्शोषण होऊ शकते.
स्क्रोटममध्ये किंवा वाहिनीच्या बाजूने जळजळ किंवा दुखापत झाल्यामुळे हायड्रोसेल्स विकसित करणे देखील शक्य आहे. एपिडायमायटिस किंवा संसर्गासारख्या स्थितीमुळे जळजळ होऊ शकते.
कोणत्या प्रकारचे हायड्रोसेल आहेत?
हायड्रोसेलचे प्रकार खालीलप्रमाणे आहेत.
- संवाद साधणारा हायड्रोसेल : हायड्रोसेलचा एक प्रकार ज्यामध्ये उदरपोकळीतील द्रवपदार्थ असतात संपर्क (संप्रेषण). संप्रेषण करणारी हायड्रोसेल प्रोसेसस योनीलिस (इनग्विनल कॅनाल आणि स्क्रोटममध्ये पसरलेली पातळ पडदा) च्या बिघाडामुळे उद्भवते. जर हा पडदा उघडा राहिला तर हर्निया आणि हायड्रोसेल दोन्ही विकसित होऊ शकतात. मुलाच्या स्क्रोटममध्ये सूज किंवा वाढ होईल, ज्याचा आकार दिवसभरात बदलू शकतो.
- नॉन-कम्युनिकेटिंग हायड्रोसेल :नॉन-कम्युनिकेटिंग हायड्रोसेल एक आहे ज्यामध्ये इनग्विनल कॅनाल बंद झाला आहे परंतु अंडकोषातील अंडकोषाच्या आसपास अतिरिक्त द्रवपदार्थ आहे. अशी स्थिती जन्माच्या वेळी उपस्थित असू शकते किंवा काही वर्षांनंतर कोणत्याही स्पष्ट कारणाशिवाय विकसित होऊ शकते. नॉनकम्युनिकेटिंग हायड्रोसेलचा आकार सामान्यतः समान राहतो किंवा खूप हळू वाढतो.
- Nuck\’s hydroceles : हा एक दुर्मिळ प्रकारचा ग्रोइनमधील लिम्फ नोड्सचा सूज आहे, जो अंडकोष नसलेल्या लोकांमध्ये येऊ शकतो. ते ओटीपोटाच्या भिंतीच्या अस्तरात येऊ शकतात. या स्थितीचे निदान करणे आणि त्यावर उपचार करणे कठीण आहे कारण हे डिम्बग्रंथि सिस्ट्स, एंडोमेट्रिओसिस आणि इतर अनेक परिस्थितींसाठी चुकीचे असू शकते.
हायड्रोसेलचे निदान करण्याची प्रक्रिया काय आहे?
अल्फा वन हॉस्पिटल येथील डॉ. खिलचंद भंगाळे चाचण्या आणि निरीक्षणांच्या संयोजनाद्वारे बालक किंवा प्रौढ व्यक्तीमध्ये हायड्रोसेलचे निदान करू शकतात, ज्यात खालील गोष्टींचा समावेश आहे:
- शारीरिक परीक्षा : यामध्ये रुग्णाला खोकल्यावर मांडीचा फुगा कसा बदलतो हे पाहणे किंवा अंडकोषातून कोणताही द्रव गोळा करणे तपासणे समाविष्ट असू शकते.
- इमेजिंग चाचणीचा वापर, जसे की अल्ट्रासाऊंड.
हायड्रोसीलमुळे कोणती गुंतागुंत होऊ शकते?
बहुतेक प्रकरणांमध्ये, हायड्रोसेल धोकादायक नाही आणि प्रजननक्षमतेवर परिणाम करत नाही. तरीही, हायड्रोसेल अंतर्निहित टेस्टिक्युलर स्थितीशी संबंधित असू शकते ज्यामुळे गुंतागुंत होऊ शकते, जसे की:
- <संसर्ग किंवा ट्यूमर : शुक्राणूंचे उत्पादन किंवा कार्य यापैकी कोणत्याही कारणामुळे कमी होऊ शकते.
- इनग्विनल हर्निया : जेव्हा आतड्याचा लूप पोटाच्या भिंतीमध्ये अडकतो तेव्हा जीवघेणा गुंतागुंत होऊ शकते.
हाइड्रोसील उपचार
हाइड्रोसील पुरुषों में अंडकोश में तरल पदार्थ भरने के कारण सूजन को संदर्भित करता है। भले ही यह कोई गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्या न हो, लेकिन यह शर्मिंदगी और परेशानी का कारण बन सकती है। वयस्क पुरुषों की तुलना में पुरुष शिशुओं में हाइड्रोसील होना अधिक आम है, और समस्या को हल करने के लिए उपचार उपलब्ध हैं।
हाइड्रोसील : यह कितना आम है ?
हाइड्रोसील लगभग 10% नवजात नर शिशुओं को प्रभावित करता है और आमतौर पर एक वर्ष के भीतर उपचार के बिना चला जाता है। वयस्क पुरुष शायद ही कभी हाइड्रोसील विकसित करते हैं, और वे अक्सर अपने आप ही गायब हो जाते हैं।
हाइड्रोसील विकसित होने का खतरा किसे है?
किशोर और वयस्क पुरुष भी इस स्थिति से पीड़ित हो सकते हैं, हालांकि यह लड़कों में बहुत अधिक आम है।
हाइड्रोसील कैसे विकसित होता है?
हालांकि हाइड्रोसील किसी भी उम्र में हो सकते हैं, वे नवजात शिशुओं में अधिक आम हैं। अंतर्निहित चोट या सूजन भी उन्हें विकसित करने का कारण बन सकती है, भले ही कोई अंतर्निहित कारण न हो। ज्यादातर मामलों में, हाइड्रोसील सिर्फ एक असुविधा है – लेकिन वे लंबे समय तक नहीं रहते हैं।
शिशुओं में
जैसे-जैसे बच्चे की गर्भावस्था आगे बढ़ती है, अंडकोष पेट से अंडकोश में उतरते हैं। उतरने पर, अंडकोष अंडकोश में होते हैं, जो त्वचा की एक थैली होती है।
एक स्वाभाविक रूप से होने वाली थैली होती है जिसमें विकास के दौरान प्रत्येक अंडकोष के चारों ओर द्रव होता है। बच्चे के पहले वर्ष के बाद, थैली स्वाभाविक रूप से बंद हो जाती है और अंदर का तरल पदार्थ शरीर द्वारा अवशोषित कर लिया जाता है। हालांकि, हाइड्रोसील वाले शिशुओं को इसका अनुभव नहीं होता है। समय से पहले जन्म लेने वाले बच्चों में हाइड्रोसील विकसित होने का खतरा अधिक होता है।
वयस्कों के बीच
40 वर्ष से अधिक उम्र के पुरुषों के लिए बाद में जीवन में हाइड्रोसील विकसित करना भी संभव है। हर्निया उनके कारण हो सकते हैं, लेकिन वे कम आम हैं। आम तौर पर, यह या तो सूजन या ट्यूनिका वेजिनेलिस से तरल पदार्थ को पुन: अवशोषित करने में असमर्थता है। थैली में उपकला कोशिकाओं के साथ शिथिलता से अतिरिक्त द्रव उत्पादन और पुनर्अवशोषण हो सकता है।
अंडकोश में या चैनल के साथ सूजन या चोट के कारण हाइड्रोसील विकसित होना भी संभव है। एपिडीडिमाइटिस या संक्रमण जैसी स्थिति सूजन का कारण बन सकती है।
हाइड्रोसील कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
हाइड्रोसील के प्रकार इस प्रकार हैं:
- संचार हाइड्रोसील : एक प्रकार का हाइड्रोसील जिसमें उदर गुहा में तरल पदार्थ होते हैं संपर्क (संचार)। एक संचार हाइड्रोसील का परिणाम प्रोसस वेजिनेलिस (पतली झिल्ली जो वंक्षण नहर के माध्यम से और अंडकोश में फैली हुई है) की विफलता से होता है। यदि यह झिल्ली खुली रहे तो हर्निया और हाइड्रोसील दोनों विकसित हो सकते हैं। बच्चे के अंडकोश में सूजन या वृद्धि होगी, जो पूरे दिन आकार में बदल सकती है।.
- नॉन-कम्युनिकेटिंग हाइड्रोसील : नॉन-कम्युनिकेटिंग हाइड्रोसील वह है जिसमें वंक्षण नहर बंद हो गई है लेकिन अंडकोष में अंडकोष के आसपास अभी भी अतिरिक्त तरल पदार्थ है। इस तरह की स्थिति जन्म के समय मौजूद हो सकती है या बिना किसी स्पष्ट कारण के वर्षों बाद विकसित हो सकती है। एक गैर-संचारी हाइड्रोसील का आकार आमतौर पर समान रहता है या बहुत धीरे-धीरे बढ़ता है।
- नक्स हाइड्रोसेल्स : कमर में लिम्फ नोड्स की एक दुर्लभ प्रकार की सूजन है, जो अंडकोष के बिना लोगों में हो सकती है। वे श्रोणि की दीवार के अस्तर में हो सकते हैं। इस स्थिति का निदान और उपचार करना मुश्किल है क्योंकि इसे डिम्बग्रंथि के सिस्ट, एंडोमेट्रोसिस और कई अन्य स्थितियों के लिए गलत माना जा सकता है।
हाइड्रोसील के निदान की प्रक्रिया क्या है?
डॉ. खिलचंद भंगले Alpha One Hospital पर परीक्षणों और अवलोकनों के संयोजन के माध्यम से एक बच्चे या वयस्क में हाइड्रोसील का निदान कर सकते हैं, जिसमें शामिल हैं:
- शारीरिक परीक्षा : इसमें यह देखना शामिल हो सकता है कि जब रोगी खांसता है या अंडकोश के माध्यम से किसी तरल पदार्थ के संग्रह की जांच करने के लिए ग्रोइन क्षेत्र में उभार कैसे बदलता है।
- एक इमेजिंग परीक्षण का उपयोग, जैसे कि अल्ट्रासाउंड।
हाइड्रोसील क्या जटिलताएं पैदा कर सकता है?
ज्यादातर मामलों में, हाइड्रोसील खतरनाक नहीं है और प्रजनन क्षमता को प्रभावित नहीं करता है। फिर भी, एक हाइड्रोसील एक अंतर्निहित वृषण स्थिति से जुड़ा हो सकता है जो जटिलताओं को जन्म दे सकता है, जैसे:
- संक्रमण या ट्यूमर : इनमें से किसी भी कारण से शुक्राणु का उत्पादन या कार्य कम हो सकता है।
- वंक्षण हर्निया : जीवन के लिए खतरनाक जटिलताएं तब हो सकती हैं जब आंत का लूप पेट की दीवार में फंस जाता है


