Gallstones Treatment
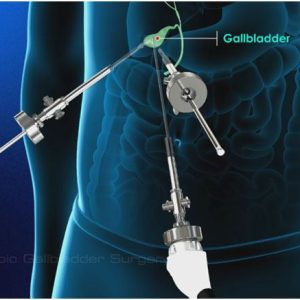
Gallstones Treatment
The gallbladder forms gallstones when bile materials become hardened. Depending on their size, they can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a ping pong ball. Generally speaking, they don\’t cause any problems, but if they move into your bile ducts, they can cause problems. Gallstones are called cholelithiasis when they occur.
Gallstones: what are they ?
Bile is stored in the pear-shaped gallbladder, where gallstones form. Concentrated bile materials form pebble-like pieces. The fluid produced by the liver contains cholesterol, bilirubin, bile salts, and lecithin. The most common cause of gallstones is cholesterol or bilirubin. This fluid collects at the bottom of the gall bladder. Subsequently, they harden and become stones.
Depending on their size, gallstones can range from the size of a grain of sand to the size of a golf ball. As extra materials accumulate and bile continues to wash over them, they grow gradually. It\’s actually the smaller stones that can cause the most problems. This is because smaller stones can move more easily than larger ones. A gallstone that travels may become stuck somewhere and become blocked.
Cholelithiasis: what is it ?
A gallstone condition is called cholelithiasis. A lot of people don\’t know they have cholelithiasis. There is no guarantee that gallstones will cause you any problems. Do not worry if they do not. It is possible, however, for gallstones to cause problems if they form a blockage in the digestive system. It will lead to inflammation and pain in your organs. It can lead to some complications if left untreated.
Gallstones: how common are they ?
Adults over age 65 and those over the age of 10 are more likely to develop gallstones. Approximately 20% of those diagnosed with gallstones will require treatment.
What are the effects of gallstones (cholelithiasis) ?
Biliary system includes your gallbladder. Bile is passed between organs through it. In order to connect these organs, bile ducts serve as conduits. Through the liver and gallbladder, bile travels on its way to the small intestine through the bile ducts. Additionally, pancreas also delivers digestive juices through them.
The passage of bile can be obstructed by a gallstone that reaches the mouth of the gallbladder. If a gallstone makes its way out of your gallbladder and into the bile ducts, it could block bile flow. This will result in bile backing up into nearby organs. Bile backup causes inflammation and pain in your liver and bile ducts when it builds up.
- Gallbladder disease :A gallbladder disease is most commonly caused by gallstones. Inflammation of your gallbladder occurs when they get stuck and cause bile to back up into it. Your gallbladder can be permanently damaged by this over time, scarring the tissues and making it dysfunctional. Gallbladder infections are also more likely when bile flow is stalled.
- Liver disease : It is possible for bile to back up into your liver if there is a blockage anywhere in the biliary system. As a result, your liver will become inflamed, increasing the risk of infection and scarring (cirrhosis). The biliary system breaks down when the liver stops working well. It is possible to live without a gallbladder, but not without a liver.
- Gallstone pancreatitis :If you have a gallstone that blocks the pancreatic duct, your pancreas will be inflamed. Your organs can be affected by inflammation temporarily and chronically, which can cause long-term damage that can stop them from working.
- Cholangitis :Bile duct inflammation can result in infections in the short term and scarring in the long run. When your bile ducts are scarred, they narrow, which prevents bile from flowing freely. Despite removal of the blockage, this can cause long-term bile-flow problems.
- Jaundice :When bile builds up in your system, it leaks into your bloodstream, causing sickness. It is bile that carries toxins from your body that have been filtered by liver. Whites of your eyes will appear yellow when your bilirubin content is high.
- Malabsorption :You may have difficulty digesting and absorbing nutrients from your food if bile can\’t reach your small intestine. In the small intestine, bile is especially important for breaking down fats and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins.
How are gallstones caused ?
Health care providers discover excess cholesterol in up to 75% of gallstones they find. Having excess cholesterol in your blood leads to gallstones, so we could say that cholesterol is the leading cause of gallstones. There are a number of reasons why you might have extra cholesterol. Obesity and diabetes are two of the most common metabolic disorders.
Your bile contains more cholesterol when your blood cholesterol is high. Before sending bile to your gallbladder, your liver filters cholesterol from your blood and deposits it in bile as a waste product. A chemical in bile (lecithin) is supposed to dissolve cholesterol. However, if there are too many of these chemicals, they might not work as well.
Gallstones can also be caused by:
- Excess bilirubin :Approximately 25% of gallstones are composed of excess bilirubin instead of cholesterol. In the process of breaking down red blood cells, bilirubin is produced as a byproduct. While your liver is performing its tasks, it can produce extra bilirubin due to certain medical disorders. The most common of these are infections, blood disorders, and liver diseases.
- Gallbladder stasis : When your small intestine needs to digest fat, it signals the gallbladder to send bile. Healthy gallbladders contract efficiently to move bile out when needed. In some cases, however, some bile may not be excreted if the gallbladder does not contract properly. Your gallbladder gradually concentrates bile into sludge that crystallizes at the bottom.
Gallstones: who gets them ?
In spite of their common occurrence after age 40, gallstones can occur at any age, including children. The reason for this is that gallstones grow very slowly. In order for gallstones to grow large enough to cause obstructions, it takes 10 to 20 years.
What makes women more likely to develop gallstones ?
Gallbladder contractions are slowed down by progesterone, and Estrogen increases cholesterol. During certain phases of your reproductive life, such as menstruation and pregnancy, both hormones are especially high. During menopause, many people use hormone therapy (HT) to replace their low hormone levels, which raises them again.
The body fat gain and loss rates are also higher for women and people born female. Blood cholesterol levels can be elevated by excess body fat. Estrogen levels increase when you are obese. Meanwhile, rapid weight loss has the same effect as weight gain. Whenever you lose a lot of body fat at once, your liver processes an unusually large amount of cholesterol, which ends up in your bile.
How do you know if you have gallstones ?
Gallstones won\’t cause any problems unless they get stuck somewhere and cause a blockage. Symptoms of biliary colic include abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen. In most cases, it occurs after a large or rich meal that lasts for one to several hours. Your gallbladder sends bile to your small intestine for digestion when it contracts.
The occasional episodes of biliary colic indicate that a gallstone is partially blocking your gallbladder, but you are not aware of it until your gallbladder contracts. As a result of the contraction, pressure is forced through your bile ducts and builds up inside your body when it encounters resistance.
Pain caused by gallstones: what does it feel like?
It is most common to experience gallbladder pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, underneath the ribs, where your gallbladder is situated. There are times, however, when you feel it in your abdomen more vaguely. There is also a possibility that the pain can radiate to another part of the body, most commonly the right arm or shoulder blade. Within the first hour, it starts as a dull ache that gradually intensifies before subsiding.
As its name implies, biliary colic does not cause sharp or waves of pain, as does colicky pain. This arc is slow and steady, and it is usually dull but severe. Additionally, you may feel tenderness in your upper right abdomen. Vomiting and nausea are often associated with biliary colic. It is also known as \”Gall Bladder Attack.”
Are there any other symptoms associated with gallstones ?
Gallstones that cause a persistent blockage or infection may cause acute inflammation symptoms, such as:
- Fever and chills.
- Constant pain.
- Heart rate accelerations.
As bile accumulates in your bloodstream, you may also experience the following symptoms :
- Jaundice.
- Dark-colored pee.
- Sunken eyes.
How are gallstones diagnosed ?
Blood tests and imaging tests will be conducted by your healthcare provider if you are experiencing biliary colic symptoms. Your healthcare provider can use blood tests to detect inflammation, infection or jaundice, as well as which organs are being affected. Imaging tests will help identify the source of the blockage. They usually begin with an ultrasound.
Keeping a healthy diet and eating in moderation
These tips can help you reduce your gallstone risk and improve your condition:
- Lessen your intake of refined carbohydrates (such as cookies and white bread).
- Eat more healthy fats, such as fish oil and olive oil, which can help your gallbladder contract and empty regularly.
- Make sure you consume enough fiber every day (women need about 25 grams a day, men need about 38 grams a day).
- Keep yourself physically active every day.
- Make sure you stay hydrated.
Weight loss should be done slowly to reduce the risk of gallstones and other health issues.
Taking preventative measures
The formation of gallstones appears to be heavily influenced by cholesterol, even though there is no foolproof way to prevent them. You might be advised to limit foods with a high saturated fat content if you have a family history of gallstones. Some of these foods include:
- cakes and cookies.
- fatty meat, like sausage and bacon.
- certain cheeses.
- lard and cream.
Maintaining a moderate weight is another way to limit the possibility of gallstones, since obese people are more likely to develop them.
मूळव्याध
मूळव्याध म्हणजे काय ?
मूळव्याध म्हणजे तुमच्या गुदाशय आणि गुदद्वाराच्या सर्वात खालच्या भागात सूजलेल्या नसा. काहीवेळा, या रक्तवाहिन्यांच्या भिंती इतक्या पातळ पसरलेल्या असतात की शिरा फुगल्या जातात आणि चिडचिड होतात, विशेषत: जेव्हा तुम्ही मलविसर्जन करता तेव्हा. मूळव्याधांना मूळव्याध देखील म्हणतात.
मूळव्याध हे गुदाशय रक्तस्त्राव होण्याचे सर्वात सामान्य कारणांपैकी एक आहे. ते अनेकदा स्वतःहून निघून जातात. उपचार देखील मदत करू शकतात.
Hemorrhoids ची लक्षणे
अंतर्गत मूळव्याध
बहुतेक प्रकरणांमध्ये, अंतर्गत मूळव्याध दिसत नाहीत किंवा जाणवत नाहीत कारण ते तुमच्या गुदाशयाच्या आत आहेत. ते सहसा दुखत नाहीत कारण तुमच्याकडे वेदना-संवेदनशील तंत्रिका कमी आहेत. अंतर्गत मूळव्याधशी संबंधित अनेक लक्षणे आहेत, यासह:
- तुमच्या मलमूत्रावरील रक्त, तुम्ही पुसल्यानंतर तुमच्या टॉयलेट पेपरवरील रक्त किंवा तुमच्या टॉयलेट बाऊलमधील रक्त
- तुमच्या गुदद्वाराच्या बाहेर फुगलेली उती. जेव्हा तुम्ही मलविसर्जन करता तेव्हा ते अनेकदा दुखते. लांबलचक मूळव्याध हे ओलसर अडथळे म्हणून दिसू शकतात जे आसपासच्या ऊतींपेक्षा गुलाबी असतात. ते सहसा त्यांच्या मूळ स्थानावर परत जातात. तसे न झाल्यास, त्यांना बर्याचदा हळूवारपणे पुन्हा जागेवर ढकलले जाऊ शकते.
प्रोलॅप्सच्या डिग्रीनुसार अंतर्गत मूळव्याध 1 ते 4 पर्यंत श्रेणीबद्ध केले जातात:
- ग्रेड 1 मूळव्याध गुदाशयात प्रोलॅप्सशिवाय राहतो (गुदद्वारातून बाहेर काढणे).
- ग्रेड 2 मूळव्याध असलेली व्यक्ती मल पास करते आणि नंतर स्वतःमध्ये परत येते.
- ग्रेड 3 चे मूळव्याध लांबलेले आहेत आणि त्यांना परत आत ढकलणे आवश्यक आहे.
- ग्रेड 4 चे मूळव्याध लांबलचक असतात आणि परत ढकलले जाऊ शकत नाहीत.
बाह्य मूळव्याध
तुमच्या गुदद्वाराभोवती आणखी अनेक वेदना-संवेदनशील नसा आहेत, जिथे बाह्य मूळव्याध स्थित आहेत. बाह्य मूळव्याध खालील लक्षणांद्वारे दर्शविले जाते:
- वेदना.
- खाज सुटणे.
- सूज येणे.
- रक्तस्त्राव.
थ्रोम्बोज्ड मूळव्याध
रक्ताच्या गुठळ्यामुळे बाह्य मूळव्याध जांभळा किंवा निळा होणे शक्य आहे. या प्रकरणात, त्याला थ्रोम्बोसिस किंवा थ्रोम्बोस्ड हेमोरायॉइड म्हणतात. येथे काही लक्षणे आहेत ज्या आपण लक्षात घेऊ शकता:
- तीव्र वेदना.pain.
- रक्तस्त्राव..
- खाज सुटणे.
तुमच्या डॉक्टरांचा सल्ला कधी घ्यावा ?
मूळव्याधशी संबंधित कोणताही धोका क्वचितच असतो. तुमची आणखी गंभीर स्थिती नाही याची खात्री करण्यासाठी, एक आठवड्यानंतर लक्षणे दूर न झाल्यास तुमच्या डॉक्टरांना भेटा.
मूळव्याध : कारणे आणि जोखीम घटक
तुमच्या पालकांसारख्या कुटुंबातील इतर सदस्यांना मूळव्याध असल्यास तुमच्यावर परिणाम होण्याची शक्यता जास्त असते. तुमच्या खालच्या गुदाशयातील रक्तवाहिन्यांना सूज येणे तुमच्या खालच्या गुदाशयात दाब वाढल्यामुळे होऊ शकते. खालील घटक त्यात योगदान देऊ शकतात:
- आतड्याची हालचाल पुशिंगसह होते
- जेव्हा तुम्ही एखादी शारीरिक मागणी करत असाल तेव्हा जड काहीतरी उचलल्याने तुम्हाला ताण येऊ शकतो
- लठ्ठपणा, किंवा जास्त वजन
- गर्भधारणेदरम्यान वाढणारे गर्भाशय तुमच्या नसांवर दाबते.
- फायबरची कमतरता असलेले आहार.
- गुदद्वारासंबंधीचा संभोग.
जे लोक दीर्घकाळ उभे राहतात किंवा बसतात त्यांना धोका वाढतो.
जर तुम्हाला बद्धकोष्ठता किंवा अतिसार दूर होत नसेल तर ते मिळणे शक्य आहे. खोकला, शिंकणे आणि उलट्या करून ते आणखी वाईट होऊ शकतात.
मूळव्याधचे निदान
तुम्हाला तुमच्या डॉक्टरांकडून तुमचा वैद्यकीय इतिहास आणि लक्षणांबद्दल विचारले जाईल. डॉक्टरांना खालीलपैकी एक किंवा दोन्ही चाचण्या करण्याची आवश्यकता असू शकते:
- शारीरिक तपासणी. तुमच्या डॉक्टरांना तुमच्या गुद्द्वार आणि गुदाशयात गुठळ्या, सूज, जळजळ किंवा इतर समस्या आढळल्यास, डॉ. खिलचंद भंगाळे त्यांची तपासणी करतील.
- तुमच्या गुदाशयाची डिजिटल तपासणी करा. स्नायूंचा टोन तपासण्यासाठी आणि गुठळ्या किंवा कोमलता जाणवण्यासाठी, तुमचे डॉक्टर स्नेहन लागू करतील आणि तुमच्या गुदाशयात बोट ठेवतील.
अंतर्गत मूळव्याधचे निदान करण्यासाठी किंवा इतर परिस्थिती नाकारण्यासाठी खालील चाचण्या आवश्यक असू शकतात:
- अॅनोस्कोपी : तुमच्या गुदद्वारासंबंधीचा कालवा तपासण्यासाठी डॉ. खिलचंद भंगाळे यांनी अॅनोस्कोप नावाची एक लहान प्लास्टिक ट्यूब वापरली आहे.
- Sigmoidoscopy : सिग्मोइडोस्कोप एक लवचिक प्रकाश असलेली ट्यूब आहे जी तुमचे डॉक्टर तुमच्या खालच्या कोलनची तपासणी करण्यासाठी वापरतात. ट्यूबसह चाचणीसाठी थोडासा ऊतक देखील घेतला जाऊ शकतो.
- कोलोनोस्कोपी : कोलोनोस्कोपद्वारे, डॉक्टर तुमच्या संपूर्ण मोठ्या आतड्याची तपासणी करतात. ऊतींचे नमुने घेण्याव्यतिरिक्त, ते त्यांना आढळलेल्या इतर समस्यांवर देखील उपचार करू शकतात.
मूळव्याध उपचार
मूळव्याधची लक्षणे सहसा स्वतःच अदृश्य होतात. तुमचे डॉक्टर सुचवतील ती उपचार योजना तुमच्या लक्षणांच्या तीव्रतेवर अवलंबून असेल
- घरगुती उपाय : साध्या जीवनशैलीत बदल करून सौम्य मूळव्याधची लक्षणे दोन ते सात दिवसांत दूर होऊ शकतात.
- नॉनसर्जिकल उपचार : ओव्हर-द-काउंटर क्रीम आणि इतर औषधे वापरून वेदना, सूज आणि खाज सुटू शकते.
- सर्जिकल उपचार : जर इतर उपचार काम करत नसतील किंवा ते मोठे असतील तर मूळव्याधांना शस्त्रक्रिया करावी लागू शकते. रसायने, लेसर, इन्फ्रारेड लाइट आणि लहान रबर बँड यासह त्यांच्यापासून मुक्त होण्याचे अनेक मार्ग आहेत. त्यांच्या आकारानुसार किंवा ते परत येत राहिल्यास, त्यांना काढण्यासाठी तुमच्या डॉक्टरांना स्केलपेल वापरण्याची आवश्यकता असू शकते.
मूळव्याध प्रतिबंध
मूळव्याध भडकणे टाळण्यासाठी येथे काही टिपा आहेत:
- फायबर खा : असे केल्याने, तुम्ही अन्न लवकर पास करू शकाल. आपण ते भाज्या, फळे, संपूर्ण धान्य, नट, बिया, सोयाबीनचे आणि शेंगा यांसारख्या वनस्पतीजन्य पदार्थांमधून मिळवू शकता. दररोज 20 ते 35 ग्रॅम आहारातील फायबर वापरा.
- फायबर सप्लिमेंट्स वापरा : जर तुम्ही अन्नातून पुरेसे फायबर घेत नसाल, तर ओव्हर-द-काउंटर सप्लिमेंट्स मल मऊ करण्यास मदत करू शकतात. सुरुवातीला थोड्या प्रमाणात वापरा आणि नंतर हळूहळू वाढवा.
- पाणी प्या :कठीण मल आणि बद्धकोष्ठता टाळून, तुम्हाला आतड्यांदरम्यान कमी ताण येईल. जास्त प्रमाणात फायबर असलेल्या भाज्या आणि फळांमध्येही भरपूर पाणी असते.
- व्यायाम :कठीण मल आणि बद्धकोष्ठता टाळून, तुम्हाला आतड्यांसंबंधी हालचाल करताना कमी ताण येईल. जास्त प्रमाणात फायबर असलेल्या भाज्या आणि फळांमध्येही भरपूर पाणी असते.
- जाण्याची वाट पाहू नका :तुम्हाला शौचालयात जाण्याची तीव्र इच्छा वाटत असल्यास, ते शक्य तितक्या लवकर करा.
- आतड्याची हालचाल करताना ताण देऊ नका किंवा जास्त वेळ टॉयलेटवर बसू नका. परिणामी तुमच्या नसा अधिक दबावाखाली येतात.
- निरोगी वजन राखा
बवासीर का इलाज
बवासीर क्या हैं?
बवासीर आपके मलाशय और गुदा के निचले हिस्से में सूजी हुई नसें हैं। कभी-कभी, इन रक्त वाहिकाओं की दीवारें इतनी पतली हो जाती हैं कि नसें फूल जाती हैं और चिड़चिड़ी हो जाती हैं, खासकर जब आप शौच करते हैं। बवासीर को पाइल्स भी कहते हैं।
बवासीर मलाशय से रक्तस्राव के सबसे सामान्य कारणों में से एक है। वे अक्सर अपने आप चले जाते हैं। उपचार भी मदद कर सकते हैं।
बवासीर के लक्षण
आंतरिक बवासीर
ज्यादातर मामलों में, आंतरिक बवासीर दिखाई या महसूस नहीं कर रहे हैं क्योंकि वे आपके मलाशय के अंदर बहुत दूर हैं। वे आम तौर पर चोट नहीं पहुंचाते क्योंकि आपके पास दर्द-संवेदी तंत्रिकाएं कम होती हैं। आंतरिक बवासीर से जुड़े कई लक्षण हैं, जिनमें शामिल हैं:
- आपके मल पर खून, पोंछने के बाद आपके टॉयलेट पेपर पर खून, या आपके टॉयलेट कटोरे में खून
- प्रोलैप्स्ड ऊतक जो आपके गुदा द्वार के बाहर उभारता है। जब आप शौच करते हैं तो अक्सर दर्द होता है। प्रोलैप्सड बवासीर को नम धक्कों के रूप में देखा जा सकता है जो आसपास के ऊतकों की तुलना में गुलाबी होते हैं। वे आमतौर पर अपने मूल स्थान पर अपने आप लौट आते हैं। यदि वे ऐसा नहीं करते हैं, तो उन्हें अक्सर धीरे से वापस अपनी जगह पर धकेला जा सकता है।
आंतरिक बवासीर को प्रोलैप्स की डिग्री के आधार पर 1 से 4 तक वर्गीकृत किया जाता है:
- ग्रेड 1 बवासीर मलाशय में बिना आगे बढ़े (गुदा से बाहर निकालना) रहता है।
- ग्रेड 2 बवासीर वाला व्यक्ति मल त्याग करता है और फिर अपने अंदर लौट आता है।
- ग्रेड 3 के बवासीर आगे बढ़ गए हैं और उन्हें वापस अंदर धकेलने की जरूरत है।
- ग्रेड 4 के बवासीर आगे बढ़ गए हैं और उन्हें वापस अंदर नहीं धकेला जा सकता है।
बाहरी बवासीर
आपकी गुदा के आसपास और भी कई दर्द-संवेदी नसें होती हैं, जहां बाहरी बवासीर स्थित होती है। बाहरी बवासीर निम्नलिखित लक्षणों की विशेषता है:
- दर्द।
- खुजली।
- सूजन।
- खून बह रहा है।
घनास्त्रता बवासीर
रक्त के थक्के के कारण बाहरी बवासीर का बैंगनी या नीला हो जाना संभव है। इस मामले में, इसे घनास्त्रता या थ्रोम्बोस्ड बवासीर कहा जाता है। यहां कुछ लक्षण दिए गए हैं जिन्हें आप नोटिस कर सकते हैं:
- गंभीर दर्द।
- खून बह रहा है।
- खुजली।
अपने डॉक्टर से कब सलाह लें ?
बवासीर से जुड़ा शायद ही कोई खतरा होता है। यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कि आपके पास अधिक गंभीर स्थिति नहीं है, यदि लक्षण एक सप्ताह बाद भी दूर नहीं होते हैं तो अपने चिकित्सक को देखें।
मूळव्याध : कारणे आणि जोखीम घटक.
आपके निचले मलाशय की नसों की सूजन आपके निचले मलाशय में दबाव बढ़ने के कारण हो सकती है। निम्नलिखित कारक इसमें योगदान दे सकते हैं:
- धक्का के साथ मल त्याग
- जब आप शारीरिक रूप से कुछ मांग करते हैं तो कुछ भारी उठाने से आपको तनाव हो सकता है
- मोटापा, या अधिक वजन
- गर्भावस्था के दौरान बढ़ता हुआ गर्भाशय आपकी नसों पर दबाव डालता है
- फाइबर की कमी वाले आहार
- गुदा मैथुन
लंबे समय तक खड़े रहने या बैठने वाले लोगों के लिए जोखिम बढ़ जाता है।
यदि आपको कब्ज या दस्त है जो दूर नहीं होता है तो उन्हें प्राप्त करना संभव है। खांसने, छींकने और उल्टी से उन्हें और भी बदतर बनाया जा सकता है।
बवासीर का निदान
आपसे आपके चिकित्सक द्वारा आपके चिकित्सा इतिहास और लक्षणों के बारे में पूछा जाएगा। डॉक्टर को निम्नलिखित में से एक या दोनों परीक्षण करने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है:
- एक शारीरिक परीक्षा। यदि आपके डॉक्टर को आपके गुदा और मलाशय में गांठ, सूजन, जलन या अन्य समस्याएं मिलती हैं, तो डॉ. खिलचंद भंगाले उनकी जांच करेंगे।
- डिजिटल रूप से अपने रेक्टल की जांच करें। मांसपेशियों की टोन की जांच करने और गांठ या कोमलता महसूस करने के लिए, आपका डॉक्टर स्नेहन लागू करेगा और आपके मलाशय में एक उंगली रखेगा।
अंतर्गत मूळव्याधचे निदान करण्यासाठी किंवा इतर परिस्थिती नाकारण्यासाठी खालील चाचण्या आवश्यक असू शकतात:
- अॅनोस्कोपी : तुमच्या गुदद्वाराच्या कालव्याची तपासणी करण्यासाठी डॉ. खिलचंद भंगाळे यांनी अॅनोस्कोप नावाची एक लहान प्लास्टिक ट्यूब वापरली आहे..
- Sigmoidoscopy : सिग्मोइडोस्कोप एक लवचिक प्रकाश असलेली ट्यूब आहे जी तुमचे डॉक्टर तुमच्या खालच्या कोलनची तपासणी करण्यासाठी वापरतात. ट्यूबसह चाचणीसाठी थोडासा ऊतक देखील घेतला जाऊ शकतो.
- कोलोनोस्कोपी : कोलोनोस्कोपद्वारे, डॉक्टर तुमच्या संपूर्ण मोठ्या आतड्याची तपासणी करतात. ऊतींचे नमुने घेण्याव्यतिरिक्त, ते त्यांना आढळलेल्या इतर समस्यांवर देखील उपचार करू शकतात.
मूळव्याध उपचार
मूळव्याधची लक्षणे सहसा स्वतःच अदृश्य होतात. तुमचे डॉक्टर सुचवतील ती उपचार योजना तुमच्या लक्षणांच्या तीव्रतेवर अवलंबून असेल.
- घरगुती उपाय : साध्या जीवनशैलीत बदल करून सौम्य मूळव्याधची लक्षणे दोन ते सात दिवसांत दूर होऊ शकतात.
- नॉनसर्जिकल उपचार : ओव्हर-द-काउंटर क्रीम आणि इतर औषधे वापरून वेदना, सूज आणि खाज सुटू शकते.
- सर्जिकल उपचार : जर इतर उपचार काम करत नसतील किंवा ते मोठे असतील तर मूळव्याधांना शस्त्रक्रिया करावी लागू शकते. रसायने, लेसर, इन्फ्रारेड लाइट आणि लहान रबर बँड यासह त्यांच्यापासून मुक्त होण्याचे अनेक मार्ग आहेत. त्यांच्या आकारानुसार किंवा ते परत येत राहिल्यास, त्यांना काढण्यासाठी तुमच्या डॉक्टरांना स्केलपेल वापरण्याची आवश्यकता असू शकते.
बवासीर की रोकथाम
बवासीर के प्रकोप को रोकने के लिए यहां कुछ सुझाव दिए गए हैं:
- फाइबर खाएं : ऐसा करने से आप खाना ज्यादा तेजी से पास कर पाएंगे। आप इसे सब्जियों, फलों, साबुत अनाज, नट, बीज, सेम और फलियां जैसे पौधों के खाद्य पदार्थों से प्राप्त कर सकते हैं। प्रतिदिन 20 से 35 ग्राम आहार फाइबर का सेवन करें।
- फाइबर सप्लीमेंट्स का उपयोग करें: यदि आप भोजन के माध्यम से पर्याप्त फाइबर का सेवन नहीं करते हैं, तो ओवर-द-काउंटर सप्लीमेंट मल को नरम करने में मदद कर सकते हैं। शुरुआत में थोड़ी सी मात्रा का प्रयोग करें और फिर धीरे-धीरे इसे बढ़ाते जाएं।
- पानी पिएं:कठोर मल और कब्ज से बचने से, आप मल त्याग के दौरान कम तनाव महसूस करेंगे। जिन सब्जियों और फलों में फाइबर की मात्रा अधिक होती है, उनमें भी बहुत सारा पानी होता है।
- व्यायाम:कठोर मल और कब्ज से बचकर, आप मल त्याग के दौरान कम तनाव लेंगे। जिन सब्जियों और फलों में फाइबर की मात्रा अधिक होती है, उनमें भी बहुत सारा पानी होता है।
- जाने की प्रतीक्षा न करें:यदि आपको शौचालय जाने की इच्छा हो, तो इसे जल्द से जल्द करें।
- मल त्याग के दौरान तनाव न लें या लंबे समय तक शौचालय में न बैठें। परिणामस्वरूप आपकी नसें अधिक दबाव में आ जाती हैं।
- स्वस्थ वजन बनाए रखें।


